How to Improve Data Center Efficiency
- Mar 8th 2022
- By

With emerging 5G and IoT/IIoT technologies and ever-increasing demand for more bandwidth, data centers are housing more power-hungry equipment than ever before. And that means more energy consumption and higher costs. At the same time, increasing regulations on energy use and the need for industries to reduce emissions are requiring data centers to become more efficient than ever. That's why the use of onsite renewable energy sources and strategies like energy use monitoring are on the rise. Data center professionals predict that nearly 20% of data center power could come from solar and wind within the next three to five years—driven primarily by large hyperscale data centers.
While many enterprise data centers don't have the means to deploy onsite renewables, they still need to reduce energy consumption without compromising productivity and digital transformation. Data centers often use Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) as an indicator of efficiency, which calculates the ratio of all the energy used by the data center to the energy used by the active equipment alone. The good news is that with advancements in data center topology, today's active equipment, and the right infrastructure components, any data center can improve efficiency. Let's take a look at six proven methods for improving data center efficiency.
1. Lower Your Power Consumption with Spine & Leaf Architecture
Two-tier spine and leaf architecture, where every leaf switch connects to every spine switch, has gained momentum over traditional three-tier switch architecture. With every leaf switch connected to every spine leaf, communication between servers does not require data to flow all the way to core switches, reducing the number of switch hops for better support of low-latency applications.
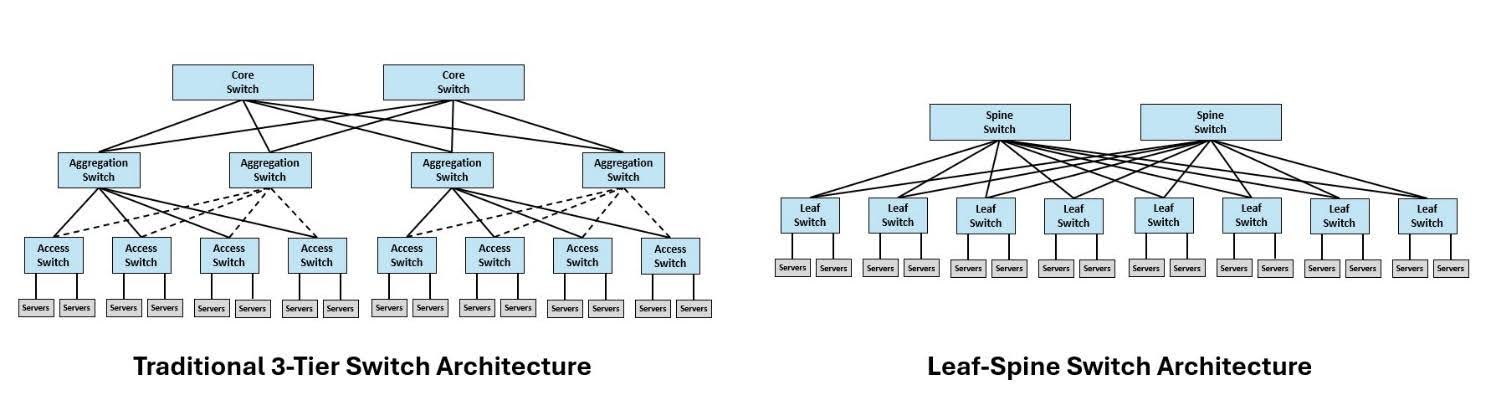
A spine and leaf architecture also improves efficiency. Having only two switch tiers in a spine and leaf architecture versus the three used in a traditional architecture eliminates an entire switch tier. Spine and leaf switches are also fixed-configuration switches that offer lower power consumption and are available with energy-efficient Ethernet that further reduces power consumption during periods of low network traffic. A typical spine and leaf switch consumes an average of 450W compared to an average of 650W for traditional modular switches. Studies show that deploying a spine and leaf architecture can achieve a 42% reduction in power consumption across an entire data center. Fixed-configuration switches are also available in smart and managed switches that offer detailed control and management over the network, including the ability to shut down inactive ports to save additional energy.
2. Reduce Cooling & Electrical Costs with High-Density Virtualized Servers
Servers and cooling systems are the highest energy consumers in the data center. Newer high-density virtualized servers replace multiple legacy servers with virtual systems. While these servers enable greater compute density in less rack space, they consume more power. However, server virtualization saves energy by significantly decreasing the overall number of physical servers and the cost to cool them.
It's estimated that consolidating just one server can save up to $500 per year in energy costs. In one study that analyzed the total cost of ownership over three years, 35 virtualized servers running on four physical host servers versus 35 physical servers without virtualization saved over $280,000, comprised of nearly $150,000 in hardware savings and more than $130,000 in electricity, cooling, server provisioning, and procurement savings.
3. Monitor & Manage Your Power with Intelligent Power Distribution
When powering active network equipment like servers and switches, filtered and protected power is typically provided by uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) and distributed via cabinet-level power distribution units (PDUs). Choosing intelligent UPS and PDUs that allow data center managers to monitor and manage power can go a long way in improving efficiency.
Metered PDUs and monitored PDUs allow for monitoring power load levels, either at the PDU or outlet level. This allows data center managers to track energy usage overtime to determine the impact of energy efficiency efforts. They can also determine which equipment to decommission or upgrade by identifying older, high-power-consuming equipment and ghost servers that are physically running and consuming energy but not performing useful functions. They can also find stranded capacity in racks or cabinets to redistribute power loads for better efficiency.

Data center managers can gain additional efficiencies by taking it one step further with switched PDUs that also allow for controlling individual outlets. This allows unused PDU outlets to be electronically shut down to shift power loads and reduce stranded power (i.e., unused power distributed to a cabinet), improving PUE. When selecting intelligent UPS, one feature to look for is bypass capability, which allows current to bypass the USP transformer and voltage regulation when utility power is normal, thus reducing energy consumption, heat generation, and operating cost.
4. Decrease Energy Consumption with Airflow Management & Advanced Cooling
Cooling accounts for nearly 40% of the total data center energy consumption. When cold intake air mixes with hot exhaust air, cooling systems like computer room air conditioner (CRAC) units and equipment fans must increase their workload to keep equipment cool. Not only does this increase the energy consumption of cooling, but it also reduces equipment reliability and leads to downtime.
Using a hot aisle/cold aisle configuration and passive aisle containment that separates cold and hot air significantly increases the savings. The Department of Energy estimates that combining a hot/aisle/cold aisle layout with containment can reduce equipment fan energy use by 20 to 25%. This included full aisle containment systems or the use of single cabinet chimneys that direct hot air into the return plenum space. There are also easy, inexpensive ways to keep cold air from mixing with hot exhaust air. Every data center manager should consider simple passive airflow management solutions like blanking panels that close off unused rack spaces to prevent mixing hot and cold air.
In addition, data center managers should consider moving to more advanced energy-efficient active cooling solutions. For example, economizers that use outdoor air and/or water for evaporative cooling can reduce energy consumption by 60% compared to standard CRAC units. Liquid cooling solutions are also more efficient than air cooling, reducing energy costs by up to 30%.
5. Avoid Additional Cooling Costs with Cabinets & Proper Cable Management

While cabinets and cable management help protect and manage equipment and cables, they are also vital to ensuring efficiency. Rather than using open racks that can hinder separating hot and cold air, cabinets with vented or solid doors are better suited for raised-floor environments and hot aisle/cold aisle configurations, including for use with aisle containment systems. Cabinets accessories like standalone fans and vented rack shelves can also help improve efficiency.
6. Save on Space with Optimal Cabling & Connectivity

While cabling and connectivity is often overlooked as a contributor to efficiency in the data center, slim jacket patch cables that use a 28 AWG construction and offer smaller overall diameter help improve airflow in and around active equipment in high-density applications, while also improving accessibility. In contrast, larger cables create more congestion within a cabinet that can impede cold air from adequately reaching equipment, requiring fans and cooling systems to work harder. Cable congestion also hinders equipment access and management.
High-density connectivity solutions like our HD8² high-density fiber optic patching system also go a long way in reducing data center space— less space to cool and operate translates to energy savings. HD8² square cassettes provide a space savings of up to 100% over traditional flat, wide cassettes. High-density connectivity also supports high-density virtualized server environments that improve efficiency.
While many enterprise data centers might not have Facebook's ability to move to 100% renewable energy or match Google's plan to be carbon-free by 2030, there are several practices and solutions that smaller data centers can adopt to improve efficiency—from switch and server consolidation to advanced power management, less energy-intensive cooling strategies, and the right infrastructure solutions.
The good news is that CablesPlus USA offers many cost-effective solutions that help improve data center efficiency, from intelligent PDUs and UPS, server cabinet fans, and blanking panels to cable management and high-density connectivity. And if you need help finding solutions that can help improve efficiency, we're always ready to help.
See Our Full Line of Data Center Solutions Contact an Expert
